In this article, the concepts of the Graining volume in batch pan and example for calculation of the graining volume are discussed.
The Concept of Graining Volume of the Batch Pan
The graining volume is the volume of the pan up to the level of the top tube plate, the minimum volume at which the pan can operate.
This term “Graining Volume” is used to denote the minimum volume of massecuite, which must be introduced in to the pan before opening of steam valve. It is calculated corresponding to the upper surface of top tube plate. It is also referred as ‘footing volume’ of the pan.
Graining volume generally expressed in percent of the working volume of the that pan. It is varies from 35 to 45%. Generally, all types of massecuites graining made with higher purity syrup or molasses and afterward pan is filled with low purity material. So lower graining volume is obviously of advantage for better purity control of massecuite. Also low graining volume is helps to increase the crystal size.
However some massecuites graining material preparation and developing of the massecuite with same material. In such situation, the % graining volume is not necessary to be considered for purity reduction.
Present scenario to improve the circulation of the pan use short length tubes . If tube length of pan decreases, then increase in the calendria diameter for the pan with same heating surface. The increase in calandria diameter increases the graining volume of pan.
In case of 800 mm tube length pans, the graining volume increases upto 40 % to 42%. Such pans definitely give higher circulation in pans.
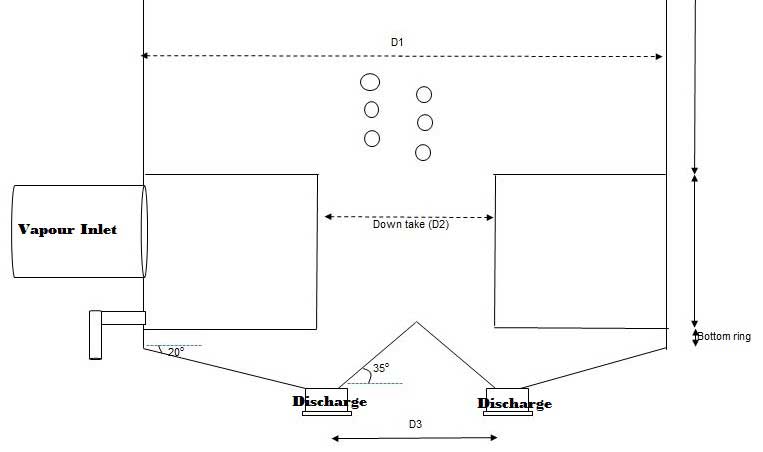
The Graining volume of the batch pan calculated by adding these volumes in pan
a) Bottom cone volume
b) Bottom ring volume
c) Total tubes volumes
d) Down take Volume
e) Volume of the pan upto 50mm height from top tube plate (It may not be required to add this volume while calculating the graining volume)
Example of calculation of graining volume single discharge type:
| Graining Volume of Batch Pan | ||||
| Sl.no. | Description | Formula | Values | UOM |
| Input Data | ||||
| 1 | Capacity of pan | 60 | T | |
| 2 | No. of tubes | N | 1306 | nos. |
| 3 | Tube thickness | t | 1.6 | mm |
| 4 | Tube Length | H1 | 750 | mm |
| 5 |
Tube OD | OD | 102 | mm |
| 6 | Dia of pan | D1 | 5600 | mm |
| 7 |
Dia of the down take | D2 | 2400 | mm |
| 8 | Height of the bottom ring | H2 | 50 | mm |
| 9 | Angle of bottom cone | α | 18 | Deg |
| 10 | Discharge Dia | D3 | 600 | mm |
| Graining Volume Calculation | ||||
| 1 | ID of the tube | ID = OD – 2xt | 98.8 | |
| 2 | Volume of massecuite in tubes | Q1 = 0.785 x ID x ID x H1 x N | 7.51 | M3 |
| 3 | Volume of down take | Q2 = 0.785 x D2 x D2 x H1 | 3.39 | M3 |
| 4 | Volume of the bottom ring | Q3 = 0.785 x D1 x D1 x H2 | 1.23 | M3 |
| 5 | Height of the bottom cone | h = [(D1 – D3)/2 ] x TAN α | 812.30 | mm |
| 6 | A1= |
0.785 x (D1)2 | 24.62 | M2 |
| 7 | A2= | 0.785 x (D3)2 | 0.28 | M2 |
| 8 | Volume of the bottom cone | Q4 = h/3 (A1+A2+√A1A2) | 7.46 | M3 |
| 9 | Graining Volume | Q1+Q2+Q3+Q4 | 19.58 | M3 |
Example of calculation of graining volume “W” type cone
| Graining Volume of Batch Pan (“W” Type cone ) | ||||
| Sl.no. | Description | Formula | Values | UOM |
| Input Data | ||||
| 1 | Capacity of pan | 60 | T | |
| 2 | No. of tubes | N | 1306 | nos. |
| 3 | Tube thickness | t | 1.6 | mm |
| 4 | Tube Length | H1 | 750 | mm |
| 5 | Tube OD | OD | 102 | mm |
| 6 | Dia of pan | D1 | 5600 | mm |
| 7 | Dia of the down take | D2 | 2400 | mm |
| 8 | Dia of bottom inverted cone | D3 | 2200 | mm |
| 9 | Height of the bottom ring | H2 | 50 | mm |
| 10 | Angle of bottom cone | α | 18 | Deg |
| 11 | Angle of bottom inverted cone | Φ | 35 | Deg |
| Graining Volume Calculation | ||||
| 1 | ID of the tube | ID = OD – 2t | 98.8 | |
| 2 | Volume of massecuite in tubes | Q1 = 0.785 x ID x ID x H1 x N | 7.51 | M3 |
| 3 | Volume of down take | Q2 = 0.785 x D2 x D2 x H1 | 3.39 | M3 |
| 4 | Volume of the bottom ring | Q3 = 0.785 x D1 x D1 x H2 | 1.23 | M3 |
| 5 | Height of the bottom cone | h 1 = [(D1 – D3)/2 ] x TAN α | 552.36 | mm |
| 6 | A1= | 0.785 x (D1)2 | 24.62 | M2 |
| 7 | A2= | 0.785 x (D3)2 | 3.80 | M2 |
| 8 | Volume of the bottom cone | Q4 = h/3 (A1+A2+√A1A2) | 7.01 | M3 |
| 9 | Height of the bottom inverted cone | h2 = [( D3)/2 ] x TAN Φ | 770.23 | mm |
| 10 | Volume of inverted cone | Q5 = 1/3 x 0.785 x (D3)2 h2 | 0.98 | M3 |
| 11 | Graining Volume | Q1+Q2+Q3+Q4 – Q5 | 18.17 | M3 |
Online Calculator for calculating the Graining Volume in Batch pan
Related Articles
Types of Graining Techniques in sugar crystallization process | Pan Boiling
B massecuite purity online calculation sheet | Sugar Technology
C massecuite final purity calculation |Grain Quantity requirement for C CVP
Melt Clarification System Design Criteria for Sugar Refinery Process
Low Grade Massecuite Treatment in Sugar Crystallization Process
Hi friends Thanks for reading this article “The concepts of graining volume in batch pan“. I Hope you liked it. Give feed back, comments and please share it.






13 thoughts on “Graining Volume Calculation in Batch Pan | Sugar Process Tech”
SARVENDRA KUMAR SRIVASTAV
(July 17, 2019 - 4:28 am)Very helpful site for the holiday.
siva alluri
(July 31, 2019 - 4:07 pm)welcome Mr.SARVENDRA KUMAR SRIVASTAV
Bandu chaure
(August 9, 2019 - 9:06 am)It is very helpful knowledge for me
Thanks sir
siva alluri
(August 13, 2019 - 2:44 pm)Welcome Bandu chaure
Shantaram Ramchandra Sahane
(February 9, 2020 - 7:33 am)Please provide a desine calculations of Sulphur burner
Shantaram Ramchandra Sahane
(April 16, 2020 - 8:36 am)Desine calculations for Sulphur burner
Rakesh Kumar
(August 21, 2021 - 12:34 am)Please provide the calculation stock law with input value
siva alluri
(September 2, 2021 - 8:27 am)Please go through the below link
https://www.sugarprocesstech.com/boiling-house-stock-calculation/
Rakesh Kumar
(August 21, 2021 - 12:37 am)It is very helpful site .
siva alluri
(September 2, 2021 - 8:26 am)Welcomr
Baraza
(January 8, 2022 - 5:54 am)Size of grain /B/C/and mass/A/B/C/seed
R.NAMASIVAYAM
(September 15, 2023 - 10:56 am)Good calculation and very use full
siva alluri
(September 17, 2023 - 1:31 pm)Thank you