Cooling and reheating Process of low grade (B & C) massecuites
The mother liquor in low grade massecuite can not be completely exhausted in vacuum pan this is due to decrease in crystallization rate and high viscosity. Final stage in sugar recovery is allowed to take place by cooling in crystalliser rather then during evaporation in vacuum pans. Because evaporation in vacuum pans is more cost effective procedure , therefore is to boil low grade massecuite in vacuum pan for limited time, then discharge it to atmospheric crystallizes followed by water cooled crystallizers.
The exhaustion of final molasses is directly related to the economy of the sugar factory and hence more attention is given being paid towards the processing of crystallisation in low grade massecuite.
The exhaustion of molasses will depend on four successive parameters.
a) Boiling a massecuite to maximum concentration in pan.
b) Cooling of the massecuite in the crystalliser to crystallise the sucrose remaining in solution.
c) Re-heating of cooled massecuite to it’s saturation temperature to reduce the viscosity of massecuite.
d) Separation of the crystals from exhausted molasses in the centrifugal machine.
To judging pan boiling operation efficiency, the use of % exhaustion and Crystal % massecuite are found more effective and informative.
Massecuite leaving a vacuum pan is supersaturated and hot, in the range 63 to 67 oC. Crystal content is high, but it is still possible to achieve additional exhaustion by cooling the massecuite prior to centrifuging. As the massecuite is cooled the crystalliztion rate rate reduces, but sufficient retention time in the cooling crystallizers will achieve the additional crystallization desired.
The ideal condition for a low-grade massecuite ” C m/c ” to crystallize more sugar from the mother liquor follow the path as illustrated in the graph below.
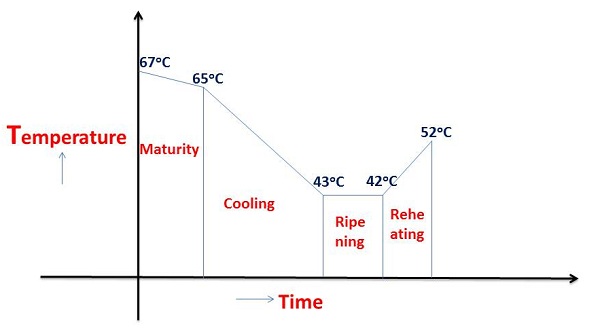 Maturity Zone: This Zone is provided without cooling arrangement and the volume of zone is designed in such a way that the retention of massecuite corresponds to 2 to 3 hrs.
Maturity Zone: This Zone is provided without cooling arrangement and the volume of zone is designed in such a way that the retention of massecuite corresponds to 2 to 3 hrs.
Cooling Zone: The Cooling zone has water cooled surface area to reduce the massecuite temperature from about 65ºC to 43 ºC within 18 to 20 hrs of time. While designing the cooling zone the ratio of S / V should be about 1.8 to 2.0 for C m/c and 1.2 for C m/c.
Ripening Zone: The Rippening zone comes after the cooling zone. This zone has no cooling water surface, but may be provided with hot water coils to take care of massecuite temp. In winter season, the retention time in this zone is about 2 to 3 hrs.
Reheating Zone : Before centrifuge the massecuite, it should be reheated upto 50 to 52ºC to reduce the viscosity and easy purging of massecuite.
Exhaustion for “C” masseuite corresponding to drop of 4 to 6 units in the purity of molasses is achieved in the crystalliser. The overall exhaustion of mother liquor in C massecuite in pan and crystalliser is shall be 24-27 units.
Exhaustion for “B” masseuite corresponding to drop of 3 to 4 units in the purity of molasses is achieved in the crystalliser. The overall exhaustion of mother liquor in B massecuite in pan and crystalliser is shall be 20-22 units.
The massecuite is dropped in a crystalliser having heating and cooling element the following treatment should be given to get the maximum exhaustion for Low Grade Massecuite .
- Leave the massecuite in crystalliser for 2 to 4 hours allowing air cooling.
- Circulate the cold water in the element so as to cool the massecuite at a rate not exceeding 1 to 2oC per hour. Quantity of cold water has to be adjusted accordingly. Temperature of cold water should be 30 to 35o .
- Cool the massecuite up to 42-43oC for C m/c and 50 to 55 oC for B m/c or till the purity of mother liquor becomes more or less constant. ( Here using Nutch apparatus to check the purity of mother liquor)
- Allow the ripening time at lowest temperature for 2 to 3 hours.
- Rate of stirring of massecuite has to be slow and not more than 0.5 rpm. ( 0.3 to 0.5 rpm for C m/c to 0.5 to 0.7 RPM for B m/c).
- Reheat the massecuite up to the saturation temperature ( 51 to 52oC ) preferably using transient heaters by using hot as a heating media.
Crystallizers generally divided in to two types as follows.
Air cooled crystallizers : It is a simple steel vessel, of “U” shaped cross-section, fitted with an agitator permitting it to maintain the mass in slow and continuous motion. open and horizontal containers type where atmospheric air is employed for cooling the massecuite.
Water cooled crystallizers : The various type of crystallisers either open or closed type where water is employed for cooling the massecuite. It can be dived furthers as Horizontal and vertical crystallizers.
The series Horizontal crystallizers with water-cooled element and vertical type crystallizers were using for this application of low grade massecuite treatment.
Related Article
Three and half massecuite boiling material balance calculation.
Three massecuite boiling solid balance calculation.
C massecuite final purity calculation |Grain Quantity requirement for C CVP

2 thoughts on “Low Grade Massecuite Treatment in Sugar Crystallization Process”
Vilas patil
(August 16, 2021 - 4:14 pm)Really valuable information sir
siva alluri
(September 2, 2021 - 8:31 am)Welcome