In this article discuss about concept and process description of Biomethanation system suitable for Distillery spent wash treatment.
Biomethanation Technology for Treatment of Distillery Effluent
Introduction:
The distillery effluent is known as spent wash and it is a highly concentrated liquid with a high organic and inorganic content. In Distillery industry spent wash treatment and disposal is one of the major issue.
Distillery effluent is having considerable organic matter which can be bio degradable. In the process of bio methanation ( anaerobic digestion ) , the bio degradable organic matter are getting converted into biogas , thus reducing the BOD level to 80 to 90% and COD level 60% to 75 %.
General Characteristics of Spent Wash in Distillery: The Spent wash parameter may be vary according to fermentation process follows in Distillery like batch, Fed batch and continuous process.
| Sr.No. | Parameter | Batch process | Fed batch process | Bio-still process |
| 1 | Volume of spent wash generation per liter of alcohol | 14 – 16 | 10 – 11 | 7 – 9 |
| 2 | Colour | Dark brown | Dark brown | Dark brown |
| 3 | pH | 3.7 – 4.5 | 4.0 – 4.3 | 4.0 – 4.2 |
| 4 | COD in mg/lit | 80,000 – 1,10,000 | 1,10,000 – 1,30,000 | 1,40,000 – 1,60,000 |
| 5 | BOD in mg/lit | 45,000 – 50,000 | 55,000 – 65,000 | 60,000 – 70,000 |
| 6 | Total Solids in mg/lit | 90,000 – 1,20,000 | 1,30,000- 1,60,000 | 1,60,000 – 2,10,000 |
| 7 | Total Volatile Solids in mg/lit | 60,000 – 70,000 | 60,000 – 75,000 | 80,000 – 90,000 |
| 8 | Total Inorganic Dissolves Solids in mg/lit | 30,000 – 40,000 | 35,000 – 45,000 | 60,000 – 90,000 |
| 9 | Chlorides (Cl) in mg/lit | 5,000 – 6,000 | 6,000 – 7,500 | 10,000 – 12,000 |
| 10 | Sulphates (SO 4) in mg/lit | 4,000 – 8,000 | 4,500 – 8,500 | 8,000 – 10,000 |
| 11 | Total nitrogen (N) in mg/lit | 1,000 – 1,200 | 1,000 – 1,400 | 2,000 – 2,500 |
| 12 | Potassium (K2O) in mg/lit | 8,000 – 12,000 | 10,000 – 14,000 | 20,000 – 22,000 |
| 13 | Phosphorus (P2O5) in mg/lit | 200 – 300 | 300 – 500 | 1,600 – 2,000 |
| 14 | Sodium (Na) in mg/lit | 400 – 600 | 1,400 – 1,500 | 1,200 – 1,500 |
| 15 | Calcium (Ca) in mg/lit | 2,000 – 3,500 | 4,500 – 6,000 | 5,000 – 6,500 |
Bio-methanation Process Description:
Bio Methanation System is based on the concept of conversion organic matter into biogas. The process of conversion of organic matter into bio gas occurs through a group of bacteria. It has to be carried out anaerobically, since the bacteria which produce methane gas from effluent are strictly anaerobes.
Here the organic matter present in the effluent gets degraded to produce methane gas. Hence here two functions are carried out simultaneously. One is the degradation of organic matter to volatile acids. The second thing is the methane gas is produced from volatile acids.
Process Flow Chart of BioMethanation system for Distillery Raw Spent Wash Treatment
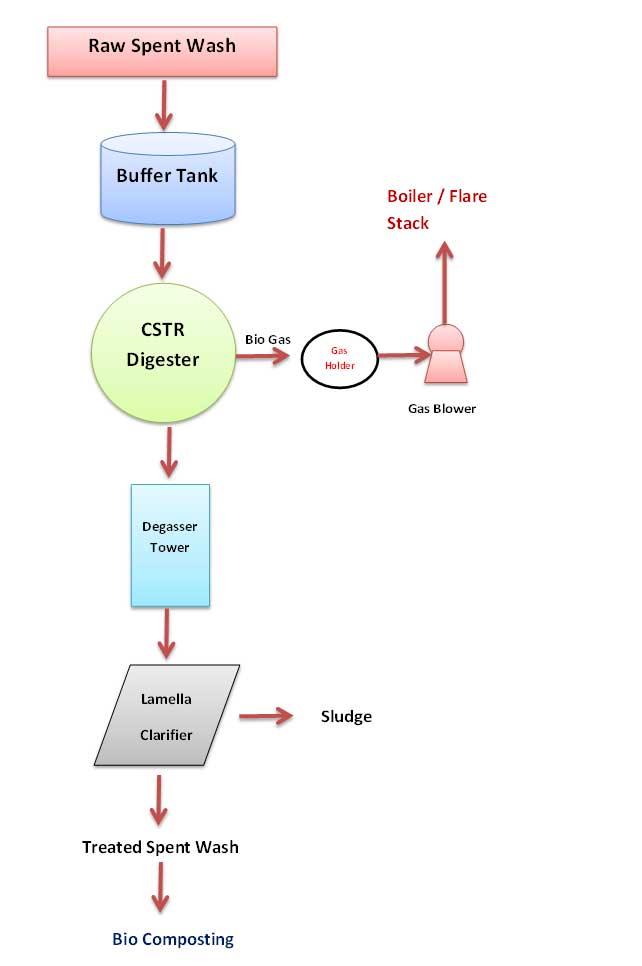 Raw Spent wash:
Raw Spent wash:
Receive the spent wash from the distillery. Further cool down of spent wash into around 40 to 45 0C temperature with plate heat exchanger and sludge settled on bottom of buffer tank.
Buffer tank:
The methane formation proceeds between pH 6.0 & 8.5. So the pH in the Buffer tank must be kept above 6.5 and reactors must be operated at a pH of 7.0 to 7.5. Some quantity of treated spent wash is recirculated to maintaining pH in buffer tank. Then spent wash fed to reactor by feed pump.
CSTR Digester:
Spent wash feed is adjusted depending upon the COD load (organic matter) in digester.
Biogas:
Bio gas will be collected at the at top of the reactor and will be stored in a floating type gasholder. Gas holder is fitted with essential safety equipment such as breather valve, flame arrestor etc. Biogas from the biogas holder will be compressed and sent to boiler used as fuel.
Treated Spent wash:
The treated spent wash from the reactor passing through degasser tower to remove gases and then sent to lamella clarifier. The solids are separated from the treated spent wash in Lamella clarifier and returned to the system by recirculation pumps. This recirculation of settled solids helps to maintained adequate population of active bacteria inside reactor. Finally treated spent wash sent to bio composting.
Bio- Gas Characteristics
Methane : 60 -65 ,%v/v
Moisture : 1 -2%
Hydrogen sulphide( H2S) : 2 -3%
Nitrogen : Traces
Carbon di oxide : Balance
Characteristics shown by spent wash after Bio gas production
Color : Blackish brown (wine red)
pH : 7.0 to 7.2
BOD : 80 to 90% reduction
COD : 60 to 70% reduction
Chlorides : 5000 mg/lit.
H2S (dissolved) : 50 mg/lit.
Potassium : 7000 mg/lit.
Temperature : 32-36 0C
The major benefits in the Biometanation Process are as follows:
1 . Low production of waste biological solids.
2. Low nutrient requirements.
3. Production of methane as an energy source of meet the steam requirement of distillery.
4. Very high loading rates can be achieved.
5. Active anaerobic sludge can be preserved unfed for many months.
Related Articles:
Basic calculation for plate type heat exchange design
Basic concepts of cooling tower, types of cooling towers and formulae
Molasses Cooler Design | Molasses Preservation | Properties of Molasses
Calculating Yield of Ethanol from Sucrose and its Process Intermediate Products
Pump Affinity Laws for Centrifugal and Positive displacement pumps


5 thoughts on “Biomethanation Process for Distillery Spent Wash Treatment | CSTR”
Rajendra Tatoba Shirdhone
(March 15, 2019 - 4:25 am)Volume of spent wash generated per litre of alcohol in batch 14-16
Which are unit for
Mandhata Patel
(April 11, 2019 - 12:03 pm)when we generate 1 lit. alcohol then 14-16 lit. spent wash is produced by the distillery Plant…….
Ajay
(June 26, 2019 - 9:07 am)Pls provide sir distillery and evaporation calculations.
Thank you sir
siva alluri
(July 2, 2019 - 2:36 pm)https://www.sugarprocesstech.com/steam-cane-quintuple/
Srivathsan
(February 10, 2021 - 1:18 am)Your feed back on subjecting bio methenated spent wash eutectic freeze crystallisation to remove majority of inorganic solids and balance liquid as feed for animals