Condensate flash vapour recovery system calculation with example
What is Flash Vapour:
The liquid suddenly passing from high pressure to low pressure condition then produces a spontaneous evaporation without any external heat energy it is called “flash” or flash vapour.
The flash vapour recovery is one of the important energy conservation system in all process industries. Simple we can say that flash pot is one of the energy conservation device.
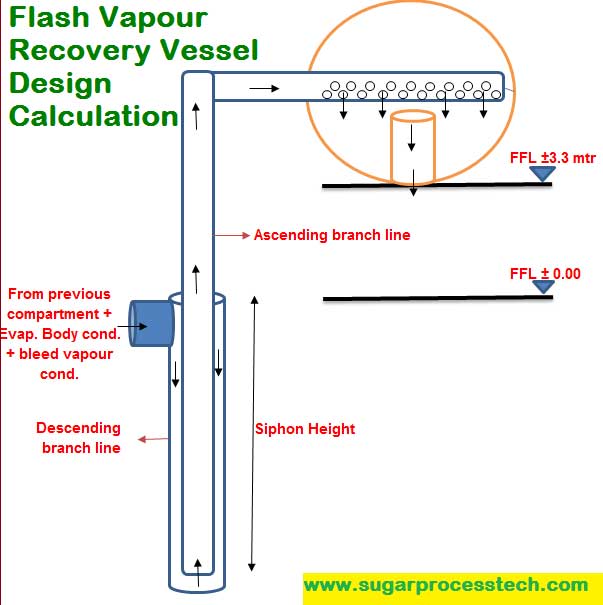
The flash pot having compartments with different pressures. The comportment connected to subsequent bodies of evaporator set.
The high temperature water suddenly pass from high pressure compartment to lower pressure compartment. It thus produces a spontaneous evaporation or “flash”, which takes place almost explosively by reason of the physical incompatibility of the conditions of pressure and temperature. The quantity of water evaporated will correspond exactly to the quantity of heat given up.
The main steps in the flash vapour recovery vessel system installation.
- Collection of the data. Find the absolute pressure of each compartment.
- Inlet and outlet water temperature with quantity for each compartment.
- Calculate the flash vapour generation quantity in each compartment.
- Find the ascending and descending branch lines dia of each compartment.
- Calculate siphon height from one compartment to next compartment.
- Finally calculate compartment area required for the flash vapour and flash vapour line dia.
In this article calculation explained by the taking with example
Here consider flash vapour system designed for 5000TCD crushing capacity plant. The flash pot for 1st , 2nd & 3rd vapours of quintuple evaporator set.
Generally, for 1st effect condensate purpose design separate flash pot or use PHE for heat recovery from that condensate water.
Find the inlet water temperature with quantity of the each compartment.
Formula for finding the evaporator body outlet condensate temperature.
Temperature of condensates
It is generally assumed that the condensates leaving a calendria are at the temperature of the vapour used in that calendria. Actually the condensates cool down slightly in running along the tubes, and their temperature may be given approximately.
Tc = Tv – 0.4 ( Tv – Tj )
Tc= temperature of the condensates leaving the calendria.
Tv = temperature of the vapour used for heating the calendria.
Tj = temperature of the juice in the vessel.
Consider 1st body calendria Absolute Pressure = 1.2 + 1.03323 = 2.23323 Kg/cm2
5 th body vapour pressure = 0.17674 Kg/cm2 (630 mm of Hg).
| ΔP Pressure difference in absolute | Pressure In absolute | Temperature in oC. | Latent heat in Kcal/kg ( λ ) | Total heat in Kcal/kg | Specific volume in M3/kg | |
| Exhust | 2.23323 | 123.1 | 524 | 647 | 0.81 | |
| 1st body | 0.4524 | 1.7808 | 115.9 | 529 | 645 | 1.01 |
| 2nd body | 0.4319 | 1.3489 | 107.6 | 534 | 642 | 1.31 |
| 3rd body | 0.4113 | 0.9376 | 97.2 | 541 | 638 | 1.84 |
| 4th body | 0.3907 | 0.5469 | 83.1 | 549 | 632 | 3.04 |
| 5th body | 0.3702 | 0.1767 | 57 | 565 | 622 | 8.76 |
For more information about calculation of pressure drop across the Multiple Effect Evaporator go through the below link
Pressure drop in Triple, Quadruple and Quintuple effect evaporator bodies with online calculator
Calculation for the 1st Compartment :
Water inlet temperature – Ti = 115.9 – 0.4 ( 115.9 – 107.6) = 115.9 – 3.32 = 112.58 oC
Water outlet temperature To = 107.6 oC
Condensate inlet Water quantity to the compartment (Q ) = 70 T/hr (As per the vapour bleeding calculation).
Specific heat of the vapour ( Cp ) = 1 Kcal/ kg/ oC
Flash Vapour generation = Q x Cp x ΔT / λ =70 x 1 x ( 112.58 – 107.6) / 534 = 0.653 T/hr = 0.653 x 1000 / 3600 = 0.1814 kg/sec = 0.1814 x 1.01 = 0.2366 M3/sec
Calculation for the 2nd Compartment :
Water inlet temperature – Ti = 107.6 – 0.4 (107.6 – 97.2) = 107.6 – 4.16 = 103.44 oC
Water outlet temperature To = 97.2 oC
Condensate inlet Water quantity to the compartment (Q ) = 70 + 63 = 133 T/hr (As per the vapour bleeding calculation).
Specific heat of the vapour ( Cp ) = 1 Kcal/ kg/ oC
Flash Vapour generation = Q x Cp x ΔT / λ =133 x 1 x (103.44 – 97.2) / 541 = 1.535 T/hr = 1.535 *1000/3600 = 0.42639 kg/ sec = 0.42639 x 1.84 = 0.784 M3 /sec
Calculation for the 3rd Compartment :
Water inlet temperature – Ti = 97.2 – 0.4 ( 97.2 – 83.1) =97.2 – 5.64 = 91.56 oC
Water outlet temperature To = 83.1 oC
Condensate inlet Water quantity to the compartment (Q ) = 70+63+31 = 164 T/hr (As per the vapour bleeding calculation).
Specific heat of the vapour ( Cp ) = 1 Kcal/ kg/ oC
Flash Vapour generation = Q x Cp x ΔT / λ =164 x 1 x ( 91.56 – 83.1) / 549 = 2.526 T/hr = 2.526 x 1000/3600 = 0.70166 kg/m3 = 0.70166 x 3.036 = 2.13 M3/sec.
Calculation of area required for flashing
The required area for flashing depend upon the flash vapour velocity at the time of generation. The Souders – Brown equation is used for calculating the maximum vapour velocity.
Velocity of flash vapour in flash tank(m/sec) = Umax = C x [ (ρ L – ρV)/ ρV]0.5
Water Density = ρ L in kg/M3
Flash vapour Density = ρ V in kg/M3
C = The value of the constant C is a measure of the droplet size that will be carried over and depends on the degree of separation of liquid and vapor required. According to Cane sugar engineering by Peter Rein , coefficient C recommended 0.01 m/s.
| Description | UOM | 1st comp. | 2nd comp. | 3rd comp. | Remarks |
| Water inlet temperature ( Ti ) | oC | 112.36 | 102.92 | 90.5 | Tc = Tv – 0.4 ( Tv – Tj ) |
| Inlet water quantity (Q ) | T/hr | 70.00 | 133.00 | 164.00 | As per the vapour bleeding calculation |
| Outlet water temperature ( To ) | oC | 107.2 | 96.5 | 81.5 | From the above table |
| latent heat of vapour ( λ) | Kcal/kg | 534 | 541 | 550 | From the above table |
| Specific volume ( µ ) | m3/kg | 1.322 | 1.883 | 3.222 | From the steam table |
| Flash vapour Quantity ( Qv ) | T/hr | 0.676 | 1.578 | 2.682 | Q x ( Ti – To) / λ |
| M3/sec | 0.24823 | 0.82519 | 2.39995 | Qv / µ | |
| Pressure difference in absolute (ΔP ) | bar | 0.4404 | 0.4195 | 0.3985 | From the above table |
| Density of water (ρ L ) | kg/m3 | 953 | 960 | 969 | From the steam table |
| Density of vapour ( ρ V ) | kg/m3 | 0.751 | 0.541 | 0.329 | From the steam table |
| Velocity of vapour in comp. ( Umax) | m/sec | 0.3561 | 0.4211 | 0.5426 | Umax = C x [ (ρ L – ρV)/ ρV]0.5 |
| Velocity of vapour ( Vv ) | m/sec | 32.5 | 35 | 40 | From Handbook of Cane sugar Engineering by Hugot |
| Compartment area required ( A ) | m2 | 0.697 | 1.959 | 4.423 | Qv / Vv |
| 1.046 | 2.939 | 6.634 | Taken 50% extra to avoid fluctuation in the body | ||
| Take Dia of the flash pot ( W ) | mtr | 2.000 | 2.000 | 2.000 | Assume as per the site condition |
| Compartment width (H = A/ W) | mtr | 1.000 | 1.470 | 3.317 | Width to be take minimum 1mtr to arrange inlet and outlet lines |
| flash vapour line dia | mtr | 0.108 | 0.190 | 0.303 | Qv = (0.785 x D2) x Vv and consider vapour 20% extra |
| mm | 125 | 200 | 300 | ||
| Velocity of the siphon descending line | m/sec | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | From Handbook of Cane sugar Engineering by Hugot |
| Velocity of the siphon ascending line | m/sec | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | From Handbook of Cane sugar Engineering by Hugot |
| Condensate descending pipe dia | mm | 200 | 250 | 275 | Fundamental formula Q = AV |
| Condensate ascending pipe dia | mm | 225 | 300 | 325 | Fundamental formula Q = AV |
| Siphon height | mtrs | 4.77 | 4.51 | 4.25 | 10.33 x ΔP / Density of the water |
| Flash vapour connection | 2nd vapour | 3rd vapour | 4th vapour |
Some Important considerations in flash pot design:
a) Flash pot is kept minimum 3 to 3.3mts from the common condensate pump for free removal of water and maintain NPSHa value for the pump.
b) Suction and delivery lines of the common condensate pump to be equalize with lost compartment of the flash pot. ( equalizing connection to be take from the top of the compartment).
c) Evaporator condensate to be connect to Descending line of the compartment. ( Evaporator 2nd body condensate line to be connect 1st compartment siphon descending line. Evaporator3rd body condensate line to be connect 1st compartment outlet line mean 2nd compartment descending line. Evaporator 4th body condensate line to be connect 2nd compartment outlet line mean 3rd compartment descending line.)
d) Pans and juice heater condensates to be connect descending branch lines of the flash pot as per the bleed vapour.
e) The inlet water line provide center of the compartment and it is to be provide throughout length of the compartment. The opening of the water to the compartment from the perforated holes only. The perforated holes area to be provide 150% of the cross section area of the in water line. The perforated holes prove only bottom portion of the pipe line.
f) The outlet water line elevation to be provide 100 to 200mm below the inlet line bottom level.
g) Generally ascending line provides in the center of the descending line. So here
Descending line cross sectional = Cross sectional area of center line ( ascending line) + Required cross section area of the water of the descending.
h) Sight and light glasses to be provide in the middle of the each compartments in opposite direction.
Some Related Articles
Condensate Receiving Tank Design Calculation | Condensate Mound | Condensate Receiving & Condensate Flash Recovery tank design
Shell and Tube Multipass Heat Exchanger Design | Tubular juice heater design calculation with online calculator
Hi friends Thanks for reading. I Hope you liked it. Give feed back, comments and please share it

21 thoughts on “Flash Vapour Calculation | Flash Vapour Recovery Vessel Design Calculation”
Bharatkumar Magdum
(October 3, 2017 - 6:28 am)Thanks madam, it is very important & valuable calculation for steam economy in sugar industry
siva alluri
(October 4, 2017 - 5:37 pm)Thank you
antonia plascencia silva
(October 8, 2017 - 2:23 am)me gustaria contar con informacion laboro en la indistria azucarera y me interresa su pagina
saluds
Emmidisetty gopi
(March 12, 2018 - 10:14 pm)Pl sale as cd for calculation purpose
siva alluri
(March 13, 2018 - 2:22 pm)Mr. Gopi
This website purely non commercial. All calculators providing in this website without any sale.
Only motive of this website to educate the all technologist to share his knowledge.
Go through the below link. In this provide list of online calculators
https://www.sugarprocesstech.com/calculators/
ASHOK KALE
(March 24, 2018 - 8:51 am)I shall require calculations for the condensate flash /sigar tank for 2500 TCD.sugar plant as working for quadruple set as both working with quintuple set .
siva alluri
(March 25, 2018 - 5:22 pm)Mr. Ashok Kale
Read this article carefully. Definitely it will give the answer for your question.
Bharatkumar Magdum
(May 17, 2018 - 8:19 am)Hallo madam
Plz give the one of the drawing of flash recovery system.
Ram Ratan Mathur
(August 4, 2018 - 5:44 pm)Sir,
I am a Sugar Technologist of 1991 batch from N.S.I. Kanpur. You have done a long time awaited wonderful
Job to our entire technocrat community. Many many thanks to you.
siva alluri
(August 13, 2018 - 2:35 pm)Thank you Mr. Ram Ratan Mathur
Jaysing patil
(June 23, 2022 - 8:52 pm)Sir please give the Continue Pan design calculation and your contact no.
siva alluri
(June 26, 2022 - 2:22 pm)Ok we will publish it soon
G.krishnamoorthy
(October 6, 2018 - 11:48 am)This website is very useful for sugar tech students for calculation & study purpose
siva alluri
(October 6, 2018 - 3:52 pm)Thank you Mr.G.krishnamoorthy
Muhammad Yaqoob Taj
(September 6, 2022 - 6:43 pm)Sir I am working in sugar factory. Plz tell me how I can calculate Siphon for FFE condensate out.
Jayawant Mohite
(October 17, 2018 - 2:48 pm)Madàm
Very very nice informaton.
siva alluri
(October 18, 2018 - 3:24 pm)Thank you Mr.Jayawant Mohite
Amit dubey
(April 22, 2020 - 6:03 am)What would be the temperature of flash vapour generated from cigar ?
Sakthivel
(March 20, 2021 - 9:06 pm)Congrats.
Chetan Vibhute
(June 15, 2021 - 10:59 am)Condensate U syphon height calculations pl
siva alluri
(June 26, 2021 - 11:51 am)It also provided in this same article