In this article provided pump related formulas like fluid flow rate and velocity, power calculation, Specific Speed of Pump (Nq), Total Head, Pump Torque and temperature rise, Net Positive Suction Head, Affinity laws for pump, Pump Efficiency & Overall Efficiency of the Pump
Basic required formulas for the operation of Pump
Formulas regarding product while pumping
Volume of the fluid (Q )
Velocity of the Fluid ( V )
Here
V = Velocity of fluid in m/sec
Q =Volume of Fluid (m3/sec)
A = Pipe line area (m2)
V = Velocity of fluid in m/sec
Q =Volume of Fluid in m3/hr
A = Pipe line dia in mm
Reynolds Number of the fluid
Here
D = Dia of the tube in meters
V = fluid velocity in m/sec
ρ= density of the fluid (kg/m3)
μ = Absolute viscosity in Pas
Absolute viscosity of the fluid (μ )
μ = υ x ρ
where:
υ = Kinematic viscosity (mm2/s)
ρ = density of the fluid in kg/m3
μ = Absolute viscosity of the fluid in mPas
Darcy Friction Factor
where:
fd = friction factor (Darcy)
Re = Reynolds number
Pump Power Calculation
Hydraulic Pump Power
The ideal hydraulic power to drive a pump depends on liquid density , differential height to lift the material and flow rate of the material.
Here
Hydraulic power in watt
Q = Flow rate in M3/sec
H = Total head in meters = Discharge head + Suction head
ρ = Density of the Fluid kg/dm3 (1 kg/m3 = 0.001 kg/dm3)
g = Acceleration due to gravity (m/sec2)
Pump Power input or Pump shaft Power
The pump power input of a centrifugal pump is the mechanical energy at the pump coupling or pump shaft absorbed from the drive.
Here
Q = Flow rate in M3/sec
H = Total head in meters = Discharge head + Suction head
ρ = Density of the Fluid ( kg/dm3)
ηp =Pump efficiency
Here
Q = Flow rate in M3/hr
H = Total head in meters = Discharge head + Suction head
ρ = Density of the Fluid ( kg/dm3 )
ηp =Pump efficiency
Pump input power from pump shaft power
Pump input power from current and voltage
Here all efficiencies are in decimals
Specific Speed of Pump (Nq)
Specific Speed of pump (Nq) is identifies the geometrical similarity of pumps. It is useful to comparing different pump designs irrespective of pump size
Nq = =
Where Nq = Dimensionless parameter
N = RPM of pump
n = Rev/sec of Pump
Q = Flow rate in m3/sec
H = Head in meters
g = Gravitational constant ( 9.81 m/sec2)
Suction Specific Speed at best efficiency point
Ns = Suction Specific speed of pump (Dimensionless parameter)
N = RPM of the pump
Q = Flow rate in M3/hr
NPSH = Net positive section head in meters
Total Head
In pumping system, Head means it is a height of a liquid coloumn.
In vertical pipe any liquid coloumn of water exerts a certain pressure (force per unit area) on a horizontal surface at the bottom area, this pressure is expressed in metres of liquid column or kg/cm2.
H = Ht – (±Hs)
where:
Ht = total discharge head
Hs = total suction head
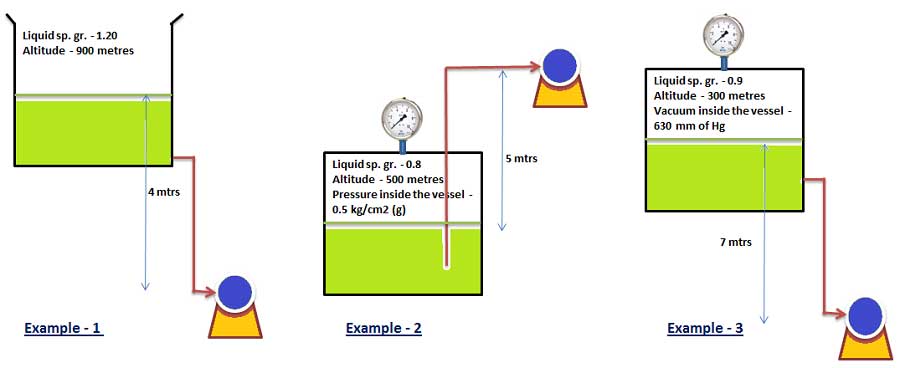
Total Discharge Head
Ht = ht + hft + pt
where:
ht = static discharge head
hft = pressure drop in discharge line
pt = Pressure head in delivery
pt > 0 for pressure
pt < 0 for vacuum
pt = 0 for open tank
Total Suction Head
Hs = hs + hfs + (± ps)
where:
hs = static suction head
hfs = pressure drop in suction line
ps = Pressure head in suction
ps > 0 for pressure
ps < 0 for vacuum
ps = 0 for open tank
Pressure Head for Pump
Pressure Head of the pump suction must be considered according to the condition of source tank.
Pressure head calculated as per pumping system source tank is under some gauge pressure or vacuum open or open to atmospheric than pressure head is calculated in metres of water column (MWC) of Feet of water column of liquid.
Velocity head
Here Hv = Velocity head in meters
V = Fluid velocity in m/sec
g = Gravitational constant (9.81 m/s2)
Q = Flow rate in m3/hr
d = pipe inside diameter in mm
Shutoff head :
Shutoff head of the centrifugal pump is the maximum head that can be developed by a pump operating at a set speed
Please go through the below link for more information about pump head
Pressure Head | Velocity head | Static Suction Head Calculation of PUMP
Pump Torque and temperature rise
Temperature rise in pumps can be calculated as per the below formula
Here
ΔT = Temperature rise in the pump (in oC)
P = brake power (kW)
ηp =Pump efficiency
Cp = specific heat of the fluid (kJ/kg oC)
Q = Flow rate of the pump (m3/second)
ρ = fluid density (kg/m3)
Net Positive Suction Head
Net Positive Suction Head Required (NPSHr ):
The amount of NPSH the pump requires to avoid cavitation is called Net Positive Suction Head Required (NPSHr). This value of the pump is determined based on actual pump test by the vendor.
Net Positive Suction Head Available( NPSHa) :
Net positive suction head available is the difference between the saturation pressure and the pump suction pressure for the liquid being pumped.
The amount of Net positive suction head available (NPSHa) to the pump from the suction line is termed NPSHa.
NPSHa = Absolute Pressure head + Static head (difference in elevation) – Vapor pressure head – Friction head loss in the piping, valves and fittings.
Net positive suction head available must be greater than or equal to the net positive suction head required to avoid cavitation. It can be stated mathematically as shown below.
NPSH a ≥ NPSH
Please go through the below link for more information about NPSH
Formulas of pump NPSH and head loss calculation in suction and delivery line
Affinity laws for pumps
Change in Diameter
D = Diameter of the impeller (inch or mm)
Q = Flow rate (gpm or m3/hr)
H = Head (ft or m)
P = Power ( hp or kW)
Change in Speed
N = Pump speed (RPM)
Q = Flow rate (gpm or m3/hr)
H = Head (ft or m)
P = Power ( hp or kW)
Please go through the below link for more information about affinity laws
Affinity laws, Affinity laws for centrifugal pumps & Positive displacement pump with example
Pump Efficiency & Overall Efficiency of the Pump
Generally for any system efficiency means the ratio of output and input
Efficiency of the system =
Pump Efficiency can be defined as a ratio of pump input and output power.
i.e Efficiency of the pump defined as the ratio of water horse power to break horse power.
Hydraulic power in Watt =
Here
Q = Flow rate in m3/sec
H = Total developed head in meters
= Density in kg/m3
Hydraulic power in kW =
Here
Q = Flow rate in Lt./sec ( 1 m3/sec = 3.6 x Lt./sec)
H = Total developed head in meters
= Density in kg/dm3 (Conversion : 1 kg/m3 = 0.001 kg/dm3)
Pump shaft power means it is an input to pump often is the output of motor.
In case of gear drive or pulley drive, efficiency of these drives will also have to be taken into account
Output of motor = (kW input to motor) x motor efficiency (ηm)
Input to motor is measured directly in kW.
Then
Pump efficiency ηp =
Overall Efficiency of the pumping system
Overall efficiency (ηoverall) = Pump efficiency (ηp) x Motor efficiency (ηm)
Overall efficiency (ηoverall) =
Related Articles:
Classification of pumps | Types of pumps and their working principles
NPSH Calculation |Head loss in suction and delivery line
Pump Vapour pressure calculation | Water Vapour Pressure Table at Different temperatures
Affinity Laws for Centrifugal and Positive displacement pumps
Pump Efficiency and Pump Power Calculation Formulas with Online Calculator
Pressure head, Velocity Head formulas with examples
Unit Conversion Factors and Tables for Engineering Design Calculations


3 thoughts on “Pump Related formulas | Power calculation, Total Head, NPSH, Affinity laws”
joel
(September 20, 2022 - 5:11 am)very handy to speed up calculation
siva alluri
(October 1, 2022 - 3:31 pm)welcome
Debasis Maitra
(December 8, 2022 - 11:07 am)Can we calculate head of a pump with the the help of impeller diameter or any other simple method for pump discharge head calculation.