Water Vapour Pressure Table at Different temperatures
Vapour pressure definition: It is the pressure exerted by the saturated vapour in contact with the surface of the liquid at that temperature. Vapour pressure is also called the vapour tension
Vapour pressure of water Concept:
All liquids have a tendency to evaporate when exposed to atmosphere. The rate at which this evaporation to atmospheric. The rate at which this evaporation occurs depends on the molecular energy of the liquid.
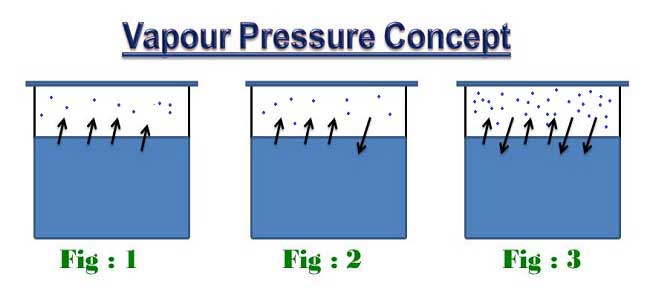 Consider a liquid contained in a sealed breaker and assume a constant temperature is maintained. In Fig – 1 some of the liquid molecules have sufficient energy to break away from the liquid and enter the air in the vapour form. As some increased container temperature the air will contain vapour molecules to the extent that some of them will be forced to re-enter the liquid by partial air pressure as shown in Fig – 2.
Consider a liquid contained in a sealed breaker and assume a constant temperature is maintained. In Fig – 1 some of the liquid molecules have sufficient energy to break away from the liquid and enter the air in the vapour form. As some increased container temperature the air will contain vapour molecules to the extent that some of them will be forced to re-enter the liquid by partial air pressure as shown in Fig – 2.
Finally in Fig- 3 an equilibrium condition will exists, when the rate at which molecules are leaving the liquid will be equal to the molecules re-entering the liquid. Under such conditions the air above the liquid is saturated with liquid molecules and the pressure on the liquid surface is called its vapour pressure at prevailing temperature.
Water vapour pressure at 100 0C is 1 atm or 1 kg/cm2 abs. at sea level.
Vapour Pressure of water versus temperature Table
Vapour Pressure table for water from 1 oC to 100 oC
| Temperature of water in 0C | Vapour pressure in bar | Temperature of water in 0C | Vapour pressure in bar |
| 1 | 0.00657 | 51 | 0.12961 |
| 2 | 0.00706 | 52 | 0.13613 |
| 3 | 0.00758 | 53 | 0.14293 |
| 4 | 0.00813 | 54 | 0.15002 |
| 5 | 0.00872 | 55 | 0.15741 |
| 6 | 0.00935 | 56 | 0.16511 |
| 7 | 0.01001 | 57 | 0.17313 |
| 8 | 0.01072 | 58 | 0.18147 |
| 9 | 0.01147 | 59 | 0.19016 |
| 10 | 0.01227 | 60 | 0.1992 |
| 11 | 0.01312 | 61 | 0.2086 |
| 12 | 0.01401 | 62 | 0.2184 |
| 13 | 0.01497 | 63 | 0.2286 |
| 14 | 0.01597 | 64 | 0.2391 |
| 15 | 0.01704 | 65 | 0.2501 |
| 16 | 0.01817 | 66 | 0.2615 |
| 17 | 0.01936 | 67 | 0.2733 |
| 18 | 0.02062 | 68 | 0.2856 |
| 19 | 0.02196 | 69 | 0.2984 |
| 20 | 0.02337 | 70 | 0.3116 |
| 21 | 0.02485 | 71 | 0.3253 |
| 22 | 0.02642 | 72 | 0.3396 |
| 23 | 0.02808 | 73 | 0.3543 |
| 24 | 0.02982 | 74 | 0.3696 |
| 25 | 0.03166 | 75 | 0.3855 |
| 26 | 0.0336 | 76 | 0.4019 |
| 27 | 0.03564 | 77 | 0.4189 |
| 28 | 0.03738 | 78 | 0.4365 |
| 29 | 0.04004 | 79 | 0.4547 |
| 30 | 0.04241 | 80 | 0.4736 |
| 31 | 0.04491 | 81 | 0.4931 |
| 32 | 0.04753 | 82 | 0.5133 |
| 33 | 0.05029 | 83 | 0.5432 |
| 34 | 0.05318 | 84 | 0.5557 |
| 35 | 0.05622 | 85 | 0.578 |
| 36 | 0.0594 | 86 | 0.6011 |
| 37 | 0.06274 | 87 | 0.6249 |
| 38 | 0.06624 | 88 | 0.6495 |
| 39 | 0.06991 | 89 | 0.6749 |
| 40 | 0.07375 | 90 | 0.7011 |
| 41 | 0.07777 | 91 | 0.7281 |
| 42 | 0.08198 | 92 | 0.7561 |
| 43 | 0.08639 | 93 | 0.7849 |
| 44 | 0.091 | 94 | 0.8146 |
| 45 | 0.09582 | 95 | 0.8453 |
| 46 | 0.10086 | 96 | 0.8769 |
| 47 | 0.10612 | 97 | 0.9094 |
| 48 | 0.11162 | 98 | 0.943 |
| 49 | 0.11736 | 99 | 0.9776 |
| 50 | 0.12335 | 100 | 1.0133 |
Vapour Pressure table for water from 102 oC to 370 oC
| Temperature of water in oC | Vapour pressure in bar | Temperature of water in oC | Vapour pressure in bar |
| 102 | 1.0878 | 200 | 15.55 |
| 104 | 1.1668 | 205 | 17.243 |
| 106 | 1.2504 | 210 | 19.077 |
| 108 | 1.339 | 215 | 21.06 |
| 110 | 1.4327 | 220 | 23.198 |
| 112 | 1.5316 | 225 | 25.501 |
| 114 | 1.6362 | 230 | 27.976 |
| 116 | 1.7465 | 235 | 30.632 |
| 118 | 1.8628 | 240 | 33.478 |
| 120 | 1.9854 | 245 | 36.523 |
| 122 | 2.1145 | 250 | 39.776 |
| 124 | 2.2504 | 255 | 43.246 |
| 126 | 2.3933 | 260 | 46.943 |
| 128 | 2.5435 | 265 | 50.877 |
| 130 | 2.7013 | 270 | 55.058 |
| 132 | 2.867 | 275 | 59.496 |
| 134 | 3.041 | 280 | 64.202 |
| 136 | 3.223 | 285 | 69.186 |
| 138 | 3.414 | 290 | 80.037 |
| 140 | 3.614 | 300 | 85.927 |
| 145 | 4.155 | 305 | 92.144 |
| 150 | 4.76 | 310 | 98.7 |
| 155 | 5.433 | 315 | 106.61 |
| 160 | 6.181 | 320 | 112.89 |
| 165 | 7.008 | 325 | 120.56 |
| 170 | 7.92 | 330 | 128.63 |
| 175 | 8.924 | 340 | 146.05 |
| 180 | 10.027 | 350 | 165.35 |
| 185 | 11.233 | 360 | 186.75 |
| 190 | 12.551 | 370 | 210.54 |
| 195 | 13.987 | 374.15 | 221.2 |
Vapour pressure of liquids at different temperatures for pump NPSH calculation
The term vapour pressure is frequently used in connection with calculation of Net Positive Suction Head available (NPSHa) in pumps.
In NPSH available calculation vapour pressure head of the liquid is very essential. It is calculated by the following formula.
Example – 1 : Calculate vapour pressure head of the gasohol at 50 0C and its specific gravity 0.8.
According to above water vapour pressure vs temperature table
Water vapour pressure at 50 0C = 0.12335 bar = 1.2335 mwc (mwc – metres of water column)
Now according to above formula
Vapour tension / vapour pressure of the liquid = 1.2335 / 0.8 = 1.54 metres
Example – 2 : Calculate vapour pressure head of the sulphited sugar syrup at 65 0C and its specific gravity 1.25
According to above water vapour pressure vs temperature table
Vapour pressure of water at 65 0C =0.2501 bar = 2.501 metres.
Now according to above formula
Vapour pressure head of the sulphited syrup = 2.501 / 1.25 = 2.0 metres.
Hi friends Thanks for reading. I Hope you liked it. Give feed back, comments and please share it
Related Articles:
Classification of pumps | Types of pumps and their working principles Classification of Dynamic Pumps | Classification of Displacement Pumps
Definitions in Steam Properties and Online Steam Table For Saturated steam

9 thoughts on “Vapour pressure of water | Water Vapour Pressure temperature chart”
Rajendra Tatoba Shirdhone
(June 24, 2018 - 5:09 pm)Good information about vapour pressure
siva alluri
(June 27, 2018 - 4:24 pm)Thank you Mr.Rajendra Tatoba Shirdhone
brijendra singh
(July 18, 2018 - 4:58 pm)good work
siva alluri
(July 22, 2018 - 4:52 am)Thank you Mr.brijendra singh
Vishnu Mehra
(April 22, 2021 - 9:53 am)Nicely explained sir. Can u tell me how to calculate water balance of sugar plant & steam balance and steam consumption?
Vishnu Mehra
(April 22, 2021 - 9:56 am)Sir kindly share notes regarding steam consumption , steam balance , water balance.
siva alluri
(April 26, 2021 - 4:01 am)Please go through the below link
https://www.sugarprocesstech.com/steam-properties/
https://www.sugarprocesstech.com/steam-cane-quintuple/
https://www.sugarprocesstech.com/pressure-drop-calculation/
Kalpesh
(July 21, 2024 - 4:07 pm)Sir,
https://www.sugarprocesstech.com/calculators/
site says page not found,
If you can Kindly share the online sugar calculators at one place.
Siva Alluri
(July 22, 2024 - 5:24 am)We will trying to rectify this issue.