Massecuite Cooling Treatment Process in Crystallizer | Sugar Tech
The massecuite when discharged from the vacuum pan is at a high supersaturation. If we have to take as advantage of this super saturation of masseccuite, it must be kept in motion to separate the sugar crystals from the mother liquor. In Crystalizers, it is a process which consists of mixing the massecuite for a certain time after dropping from the pans, and before passing to the centrifugals. Which aims at completing the formation of crystals and forcing further exhaustion of the mother liquor.
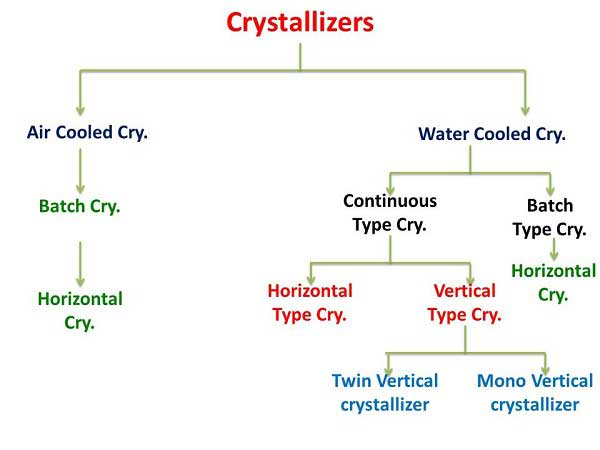
Crystallization in motion is a process in which the masecuites are slowly stirred while they cool from pan dropping temperature to one nearer to surrounding atmosphere temperature. Progressive cooling reduces the solubility of sugar and forced crystallization to continue. Continuous stirring minimizes the internal differences in temperature and super saturation and this reduces the danger of false grain formation. The above process is carried out in special equipment called as crystalliser.
These are ” U “ shaped or circular in diameter, open and horizontal containers. The stirring device consists of central shaft fitted with stirrer arms. The massecuite is cooled by air by radiation through walls of crystalliser and through the surface of crystalliser. The cooling action is very slow. These types of crystallisers are usually used for high grade massecuite.
Water Cooled Crystallisers:
The various type of crystallisers either open or closed type where water is employed for cooling. In this type of crystalliser for cooling of massecuite by circulating the water in coils or disk type elements in a proper way and cooling surface is direct contact with the entire massecuite.
Batch Type Crystallizers:
Batch crystallizers are generally horizontal type stirred vessels. Normal batch processing practice entailed gravity flow from pan, to crystallizer and then to centrifugal. Batch type crystallizers are cylindrical or ‘U’ shaped vessel equipped with slow speed stirring element.
It is applicable for high grade massecuites ( A m/c & Refined masseuites) and also it installed as a receiving crystallizers for low grade massecuite before entering to cooling crystallizers.
Continuous crystallizers :
To overcome the some disadvantages in case of low grade massecuite cooling, introduced the continuous crystallizers. With the advantages of continuous pans and continuous centrifugal machines it makes more sense to run the crystallizers as a continuous system. In continuous crystallizer, the full capacity of the crystallizers is utilized at all times. Batch type cystallizers joined in series to convert the continuous process or used vertical type designs is used for this application.
The treatment process of the various massecuites (A, B & C m/c ) follows as below
High Grade massecuites ( A m/c , Refined massecuited )
a) The speed of Rotation of stirrer should be 60 RPH.
b) Cooling hours shall be 2 to 3hrs for A m/c and less than 2hrs in case of refined massecuite.
c) The Air cooled crystallizers shall have stirring arrangement only used for this application.
d) The water cooled crystallizers not required for high grade massecuites.
B – Masseccuite
a) The speed of Rotation of stirrer should be 30 to 40 RPH.
b) The massecuite treatment hours shall be 10 to 12 hrs
c) The Air cooled crystallizers used as a receiving and maturity of massecuite purpose. And then sent to water coiling crystallizers.
d) The Water cooling crystallizers used for coolling the masseccuite from 65 to 55ºC in 8 to 10 hours.
e) The S/V ration maintained 1.2. ( S = Cooling surface area & V = Volume of massecuite).
f) The inlet cooling water to crystallizer may be considered as ambient temperature at 30 to 35ºC.
C – Masseccuite
a) The speed of Rotation of stirrer should be 20 to 30 RPH.
b) The massecuite treatment hours shall be 22 to 24 hrs
c) The Air cooled crystallizers used as a receiving and maturity of massecuite purpose. And then sent to water coiling crystallizers.
d) The Water cooling crystallizers used for coolling the masseccuite from 65 to 42ºC in 20 to 22 hours.
e) The S/V ration maintained 1.8 to 2.0. ( S = Cooling surface area & V = Volume of massecuite).
f) The inlet cooling water to crystallizer may be considered as ambient temperature at 30 to 35ºC.
Heat Transfer Coefficient (HTC):
Heat coefficients in B and C massecuite crystallizers are very low, particularly when high brix are cooled to low temperatures. These values are strongly dependent on the condition of the massecuite. Apart from the massecuite conditions, the heat transfer rate will also depend on the amount of shear applied to the cooling surfaces.
Typical values of heat transfer coeeficient for water cooled crystallizer given below as per E.Hugot.
A massecuites – 40 to 60 Kcal/m2/hr/oC
B massecuites – 35 to 50 Kcal/m2/hr/oC
C massecuites – 25 Kcal/m2/hr/oC
The HTC value for Air cooled crystallizers used by Manufacturers – 7 Kcal/m2/hr/oC
Crystallizer Capacity Calculation
Crystallizers capacity requirement calculated according to its massecuite cooling time and existing pan capacity.
According to different Authors, the capacities of Crystallizers are as follows
Noel Deer – 5 m³/TCH
Tromp – 4.44 m³/TCH.
Hugot – 6.05 m³/TCH.
Capacities of Crystallizers for 5000 TCD plant (230 TCH @ 22hours basis)
Assume the massecuite % cane
A – Massecuite – 30%
B – Massecuite – 13%
C – Massecuite – 8%
The capacity of Crystallizer will be 10% more than pan capacity (For example if pan capacity is 60 Tons, then the Crystallizer capacity should be 70 Tons each).
A massecuite quantity = 230 x 30 % = 69 T/hr ≈ 70 T/hr.
B massecuite quantity = 230 x 13 % = 29.9 T/hr ≈ 30 T/hr.
C massecuite quantity = 230 x 8 % = 18.4 T/hr ≈ 20 T/hr.
Generally manufactures taken Cooling time and curing time as follow as
| Massecuite | Cooling Time in hrs | Curing Time in hrs | Total no. of hrs |
| A | 2 | 2 to 3 | 4 to 5 |
| B | 8 | 2 to 4 | 10 to 12 |
| C | 20 | 6 to 8 (Ripening cum curing) | 26 to 28 |
Air cooled Crystallizes for A massecuite :
Total Capacity required = 70 x 4.5 = 315 T
If Batch pan capacity is 60T each then consider 70T capacity crystallizers
= 315 / 70 = 4.5 .
So consider 4 to 5 no.s of crystallizes with 70T capacity each.
Air cum Water cooled Crystallizes for B massecuite :
Total Capacity required = 30 x 10 = 300 T
If continuous pan used for B massecuite then consider receiving crystallizer of 40 to 60T capacity air cooled type and remaining capacity consider as water cooled crystallizers. It may series of horizantal type (80T x 3no.s) or vertical type with cooling element.
Air cum Water cooled Crystallizes for C massecuite :
Total Capacity required = 20 x 28 = 560 T
For continuous pan massecuite receiving purpose consider 60T capacity air cooled crystallizer. The remaining 500T capacity consider as water cooled crystallizers. Generally for “C ” massecuite purpose consider as vertical type crystallizers with cooling and heating element.
Sugar Tech Articles :
Low Grade Massecuite Treatment in Sugar Crystallization Process
Melt Clarification System Design Criteria for Sugar Refinery Process
Formulas of pump NPSH Calculation |Head loss in suction and delivery line
Sulphurless sugar concepts in sugar industry | Sugar Technology
Hi friends Thanks for reading. I Hope you liked it. Give feed back, comments and please share it

7 thoughts on “Crystallizers Application in Sugar Industry | Crystallizer Capacity Calculation”
Patil shivaji Shankar
(August 9, 2018 - 4:08 pm)Vry help ful for technologists
siva alluri
(August 13, 2018 - 2:33 pm)Thank you
Alaquanic
(August 30, 2018 - 12:30 pm)ALAQUA will supply equipment for installation by customer, skid mounted, or as turnkey projects.
Alaquainc
(January 30, 2019 - 1:02 pm)Hi, Thank you for sharing,I really like article and great information.keep it up
siva alluri
(February 3, 2019 - 2:48 pm)Thank you
Ravi Kalal
(May 11, 2019 - 10:45 am)Please tell me what is rpm for A pug mill??
David
(September 30, 2022 - 2:35 pm)I read somewhere that factors that influence sugar crystal formation include degree of supersaturation, agitation and cooling rate. i always wanted to know what the cooling rates were, thanks for the inforamtion!!!!