Vacuum Filter Operation in sugar industry | Optimization of Sugar Loss from Filter Cake
Abstract: Rotary drum vacuum filters have been widely used in sugar and a variety of other industries for
many years. They are well suited to applications where both dewatering and washing are required and appear to be the best of the available equipment for the treatment of cane sugar muds. In this article discussed about vacuum filter description, its operational parameters and also explained optimization of filter cake pol (sugar loss from vacuum filter).
Accessories of Rotary Vacuum Filter:
- Mud Mixer or bagacillo mixer.
- Mud Trough
- Rotary Filter Drum
- Two number of filtrate receivers (High vacuum and low vacuum receivers)
- Vacuum Regulating valve
- Filtrate pump
- Vacuum pump of adequate capacity & One barometric condenser
- One entrainment separator
Mud Mixer or bagacillo mixer
The mud to filters flows by gravity from the clarifier to mixer or by pump. In mixer fitted with sttirrer, bagacillo from mill baggase carrier is fed continuously to the mixer. The mixture of mud and bagacillo is continuously feed to the mud trough of filter. The RPM of the mixer is around 20 to 25.
Mud Trough & Agitator
The mud and bagacillo mixture is continuously feed to mud trough from the mud mixer. It is a semi cylindrical in shape. In order to avoid allowing the muds in the filter tank to settle out, they are kept in movement by an agitator oscillating to and fro, pivoted on the axis of the filter, and driven by a separate small motor.
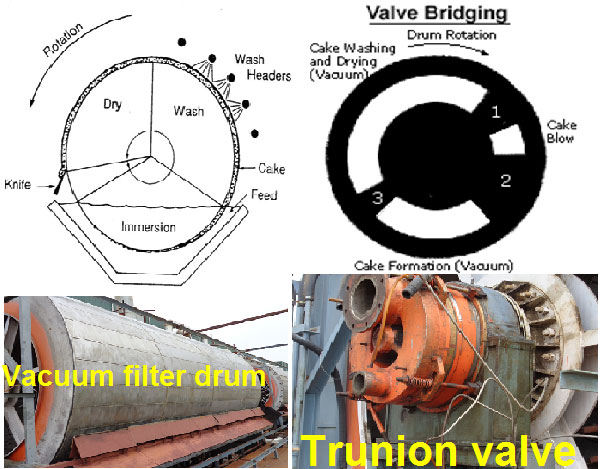
Rotary Filter Drum
The filter drum rotates around horizontal axis is always partially submerged in the mud trough. It is horizontal cylinder with corrugated surface. Which is covered by fine copper or s. s. screens. The screen has 625 perforations per sq. inch. with 0.5mm dia and 23% clear opening area.
Filtrate Receiving Vessel
All segment tubes are united in trunnion valve through which filtrate withdrawal pipes are drawn and led to filtrate connecting vessels under vacuum. One vessel for heavy and other for light filtrate. Low vacuum maintained through control valve. Top side is connected to vaccum pump for extraction of air and vapour to create vacuum. Bottom side pipes are immersed in the sealing tank.
Vacuum Pump & Condenser
Vaccum pump create vaccum inside the system. it’s capacity is about 18 meter cu air suction per square meter of filter area. The condenser condenses the vapour sucked from the filtrate the pump located near treated juice receiving tank.
- As per Peter Rein Approximately for 100m2 filter area required Vacuum pump capacity – 520 to 680L/sec and Condenser cross section area- 0.48m2 required.
Entrainment Separator
Entrainment into the filter condenser is not normally a problem if the filtrate tank cross-section area is sufficiently large, the filtrate entries directed tangentially downwards into the tank, and the gas vent to the condenser taken from the highest point in the tank. However, vacuum Leaks in the filtrate pump seals and tanks have to be avoided. Some sources recommend that filtrate pipes be of corrosion-resistant material, and that a generous head drop be
arranged between the filtrate receivers and the filtrate pumps.
Typical Analysis of Filter Drum Working :
Surface of drum is equally distributed in 24 nos. Segments having following distribution criteria for flow flowing activites table clearly indicate that by in design. Now the surface area is distributed for different activities. At the same time. The retention time for each activity may be easily allocated for efficient operation.
| Activities | Surface area % wise | Vacuum Distribution | Retention time | Nos. Tubes | Area in radius |
| Formation of cake | 16% | 8” low | 40 sec | 4 Nos. | 600 |
| Build up of cake | 16% | 8” low | 40 sec | 4 Nos. | 600 |
| Washing of cake | 33% | 15” high | 80 sec | 8 Nos. | 1200 |
| Drying of cake | 17% | 15” high | 40 sec |
4 Nos. | 600 |
| Discharging of cake | 18% | 0” low | 40 sec | 4 Nos. | 600 |
| Total | 100% | 24 no.s | 3600 |
General Operational Parameters for vacuum filters:
The settled mud from the clarifier with 6.8 to 7.0 pH and 22 to 24 Bx contains the muddy juice temperature above 80OC. For better filtration temperature should be on higher side. As viscosity of juice is inversely proportional to temperature. Low viscosity favors the filtration.
- % Pol in F.C =1.5 to 2.5
- % Humidity in F.C = 70 -80
- High vacuum = 350 to 450 mm of Hg
- Low vacuum = 200 to 250 of Hg
- Cake thickness = ¼ – ½ inch
- Wash water pressure = 2.0 -2.5 kg/cm2
- Wash water temperature = 60 – 75OC.
- Speed rotation = 3 – 5 min. per rotation
- Amount of bagacillo = 5 – 7 kg per ton of cane
- Wash water % filter cake = 150% max.
- F.C % cane = 3 – 5 % on cane
Example for calculation.
Taken one example for 8000TCD plant
Vacuum filter requirement:
Crushing Rate – 8000TCD (360 TCH for 22 hours)
Vacuum filter screen area requirement – 0.6 m2/TCH
So screen area required – 216 m2 ( i.e for example 12Ft x 24Ft size vacuum filters 3 no.s required 3 x 84m2 = 268m2)
Production of filter cake:
Production of filter cake will be 60 to 75 Kg/hr/m2 screen area and the average is 67.5 Kg/hr/m2 .
Total production of filter cake for 360TCH would be =216 X 67.5 =14.58 T/hr ( Filter cake % cane is 4%)
For 268 Sq. Mtrs it would be 18 to 20 T/Hr. ( which is equivalent to our FC % cane of 4.5 to 5%)
Bagacillo Requirement:
Quantity of Bagacillo required = 6 to 8 Kg/TCH
Quantity of Bagacillo required for 360 TCH plant =360 X 7 Kg/hr =2520 Kg/hr
Bagacillo screen Area Requirement:
General Consideration value for bagacillo for 5mm hole dia screen having 65 kg/m2/hr.
Screen Area required for bagacillo = 2520/65 = 38.76m2
Wash Water Requirement:
Wash water requirement for filters is 4 to 6% on cane or 150% on cake.
For 360 TCH plant, the wash water requirement would be =360X 0.06=21.6T/hr
Criteria for Efficient Running or Optimization filter cake Pol.
Vacuum ( Low and High vacuum levels).
Low vacuum: 8 to 12’’
• Function: Formation and build up of cake.
• If too low: Filter cake will either not form or will not have the necessary consistency. when washing the cake with water under pressure from the sprays, the filter cake will drop off the screens which affect the filter operating capacity.
• If too high: More solids goes through the heavy filtrate and screens will be chocked.
High vacuum : 15 to 20’’
• Function : Washing and drying of cake.
• If too low: The washing and drying the cake would be deficient. This would results in filter cake with high sucrose.
• If too high: Filtrate would be more cloudy and there would be a tendency for the screens and suction tube to clog.
Bagacillo
Bagacillo Act as a filtering medium and increase the porosity of cake. Hence bagacillo should be uniform in size and is adequate quantity. Bagacillo quantity will depend on the texture or density of mud. If the mud is too diluted it will be necessary to apply more bagacillo and vice versa.
a) Normally the quantity of bagacillo is from 6 to 8 Kg per ton of cane crushed.
b) Excess of bagacillo reduce the operating capacity of the filter. Adversely affect the exhaustion the filter cake and increase the polarization and sugar losses.
c) Lower bagacillo quantities reduces the filtering action. The filtrates are a lot of more cloudy and it may cause clogging of the screens and suctions tube due to the greater amount of solids that pass with the juice. The action of the scrapper is also affected which does not clean the screens.
Washing of Cake
a) Remove the sugar from the cake by displacement principal.
b) Quantity of wash water 150% on filter cake and wash water pressure of around 3 Kg/cm2 .
c) Part of soluble impurities are picked up during the washing. Resulting is a drop in purity of the juice reaching the filter and the clear filtrate leaving it. This drop is generally of the order of 2-4 units.
Wash water temperature maintained 60 to 650C.
a) To achieve an efficient exhaustion of the sucrose & less Wax in the filtrates.
b) If temp is high: Extract a larger amount of undesirable impurities, more wax will enter in the process, affecting the filter ability and quality of commercial sugar.
c) If temp is low : Desugarisation the filter cake is not achieved,results higher pol in filter cake.
Speed of the drum: 3 to 5 min per revolution.
a) If bagacillo application constant.
b) If too slow: The filter cake is too thick which would result in higher pol.The mud volume should be increased ,reduce the capacity.
c) If too high :exhaustion and washing should not be proper.
Thickness of Filter cake – 1\4” to1\2”.
a) If too much:- the exhausting of the sucrose in the mud is less ,the pol in mud will be higher and sugar losses will be greater .
b) If too thin :operating capacity of the filter is adversely affected more.cloudy filtrate, risk of clogging in the screens and suction tubes.
Mud Temperature & Trough Level:
80-850C after the addition of the bagacillo. Below that temp there is a risk of waxes blocking the gauge.
If trough level is higher, the cake should be thin.
If trough level is lower, the cake should be thick.
General Causes of mud trouble in Juice Clarifier
- Low vacuum & unsatisfactory working of filters.
- Lower P2O5 content in juice
- Faulty addition of flocculent dosage
- Poor mill sanitation
- Excessive staling of cane
- Over matured or deteriorated cane
- Diseased cane
- Poor quality lime
- Higher brix of mixed juice
Cane Quality
a) The cane quality is first important aspect while discussing the mud settling rate.
b) The cane shall be free from all extraneous matter as far as possible. In some sugar mills, cane quality is given prime importance and cane received is almost free from extraneous matter. In such situation definitely the mud settling rate is always good.
c) In case of flood affected cane may also lead to higher mud level in clarifier. A cane washing laundry as being practiced in number of countries where mechanical harvesting is practiced may be helpful for maintaining lower mud level in clarifier.
d) The cane washing is helpful for removal of mud, sand and other extraneous matter which decreases.
e) The cane shall be fresh as far as possible. The cane staling time shall not be more than 48 hours. Considering the recovery, the cane staling shall not be more than 24 hours.
f) The stale cane is increases microbial products such as dextran in cane juice. These products are not settled easily in clarifier and increase the turbidity as well as colloids in clear juice.
Mill Sanitation
a) At mills, the growth of microbes shall be controlled well. It is generally observed that the microbes grow well at various corners and surrounding of mill station as the cane juice is excellent medium for growth of microbes.
b) Leconostock mesenteriods at dead pockets of mill juice gutters, cane carrier chains, mill inter carrier chains etc.
c) Advisable to have permanent steam washing arrangement for chains of cane carrier and mill inter carriers.
d) Washing of mill surrounding and dead pockets of juice gutters shall be made twice in a shift so as to resist the microbial growth and to reduce microbial growth products in extracted juice.
e) DSM screens or rotary juice screens are also one of the important station for growth of microbes and shall be paid due attention for cleaning and washing.
Effect of Imbibition Water
High temperature imbibition water (max. 700C) is also helpful for reducing microbial population as well as microbial products in the extracted juice. At the same time the high temperature water will help in extracting more sugar. Higher % of imbibition water is useful for reducing mud level by reducing the brix % of clear juice.
Muddy Juice pH
a) It is general opinion that bacterial activity is reduced at higher temperature. But recently it has been established that some thermophillic bacteria continue their activity even at 100oC.
b) If muddy juice remains stagnant for long time in clarifier then such incidents are noticed. The drop in pH below 6.5 of muddy juice is the indication of microbial activity. In such case, the muddy juice becomes highly viscous and filter cake porosity decrease to a great extent.
c) To combat such problem it is beneficial to increase muddy juice pH above 8.0 and to process of all muddy juice with in minimum time possible.
d) This should be done immediately either by reducing crushing rate or in extreme cases by mill stoppage.
Sulphited Juice Temperature
a) The temperature of sulphited juice before flash tank should be 1020C plus.
b) It is observed that in some factories the mud trouble is a result of lower temperature of sulphited juice due to scaled juice heaters or short circuiting of sulphited juice and raw juice. The short circuiting of juice is either due to faulty double beat valves or bent juice heater lids.
Summery :
Author : Sudheer Godavarthi , KCP SUGAR & INDUSTRIES CORPORATION LIMITED
Short Description : Accessories of Rotary Vacuum Filter and its operation in sugar industry | Criteria for Efficient Running or Optimization of filter cake sugar Loss | General Causes of mud trouble in Juice Clarifier
Rotary vacuum filter Equipment capacity details in sugar industry | Rotary Vacuum Filter Accessories Capacity Calculation |Sugar Tech
Role of Bagacillo in vacuum filter | bagacillo cyclone Capacity Calculation | Bagacillo Screens, blower & Bagacillo Cyclone Sizing Calculation
Thumb Rules for Sugar factory Equipment Design Sizing | Sugar Industry Thumb Rules for Equipment Design Sizing
Sugar Industry Equipment Design and Drawing Online Calculations.
Sugar Technology online calculators | Sugar Industry capacity & Equipment Design and Drawing(EDD) online calculation sheets | sugar process technologies.
Sulphur Melter | Sulphur Melting process in sugar processing industry
Juice Defecator and Juice Sulphitor Design Criteria | Online Calculator
Hi friends Thanks for reading. I Hope you liked it. Give feed back, comments and please don’t forget to share it

22 thoughts on “Vacuum Filter Description in sugar industry | Optimization of Sugar Loss”
Suryakant Takawane
(June 26, 2017 - 6:36 am)Nice
Awanish kumar
(July 21, 2017 - 10:15 am)Sir please confirm press mud density, generated from RVF.
*Raghvendra Srivastava
(August 14, 2017 - 1:47 am)I want on line calculation
siva alluri
(August 17, 2017 - 3:56 pm)thank you sir
In next revision of this article we will provide online calculator
A P Bhatt
(August 21, 2017 - 5:53 pm).785Dia*Dia*velocity= Valume flow rate
MAHESH R
(October 17, 2017 - 6:42 am)It’s super
siva alluri
(October 19, 2017 - 12:02 pm)Thank you
Neeraj kumar rajput
(October 19, 2017 - 7:07 am)Sir what is the angle of mud trough please reply
Answer a short period
siva alluri
(October 19, 2017 - 12:22 pm)Mud trough angle depend upon vacuum filter drum dia. According to drum dia trough dia will be provided.
Ikenna Iheanacho
(October 21, 2017 - 3:21 am)Illuminating piece. thank you
BAHMED
(March 8, 2018 - 11:48 am)I can have the analysis of the turbid filtrate liquid and the nature of the solids, their size and their content? Thank you
siva alluri
(March 8, 2018 - 3:18 pm)The “www.sugarprocesstech.com” invites to all sugar technologists to share your knowledge, achievements in your working organization and new developments and technologies in sugar industry and its concerned units. It is very much helpful to show your identity to the world at the same time it will helpful to another technologist to enhance their insight and enhance great execution in there working.
sugarprocesstech@gmail.com
Salman
(April 2, 2018 - 6:04 am)I want to know for angular distribution of hi, low and no zone of rotary vacuum filter.
siva alluri
(April 6, 2018 - 1:40 pm)Read this article to know the angle distribution
https://www.sugarprocesstech.com/rotary-vacuum-filter/
Deshraj singh
(June 9, 2018 - 1:55 pm)Thanks
siva alluri
(June 13, 2018 - 5:35 pm)Thank you Mr.Deshraj singh
Aseem Kumar
(December 20, 2019 - 7:24 am)Hello Sir, Lekh padkar achcha laga, But I need Everyone , start to Cane yard , Deficater , quard, Magma mixer , Raw sugar ,Raw pan, MCS/SCS, Refinery , Refinery pan se Suger FBD , tak ki jankari chahiye, Prosses oprate system with pictures please send me,
Thank you.
WhatsApp:-. 07457876717
or email :-
aseemkumar93@gmail.com
ARVIND RATHI
(June 27, 2020 - 5:12 pm)Thanks for giving important information. Pl give calculation for Vacuum pump requirement
siva alluri
(June 28, 2020 - 12:22 pm)Welcome Mr.ARVIND RATHI
ARVIND RATHI
(June 27, 2020 - 5:14 pm)Thanks for giving imp knowledge
Vishvjeet Pundir
(August 15, 2020 - 12:07 am)What is the important characteristics of muddy juice which take play an important role in filteration in the sense of chemistry
Surya - 7729056998
(January 13, 2023 - 12:23 am)Dear patrons,
I wish to notify you that we have 4 sets of vaccum filter drums which we have purchased from KCP sugars challapalli which are available for sale – kindly WhatsApp me for images and sale price.
Best regards
Surya – 7729056998