Role of Flocculants in Sugar Industry | Flocculant Dosing Online Calculator
Introduction of flocculants:
Flocculants are a reagent added to a dispersion of solids in a liquid to bring together the fine particles to from floc.
The flocculants are generally classified as natural flocculants and Synthetic flocculants.
Natural Flocculants:
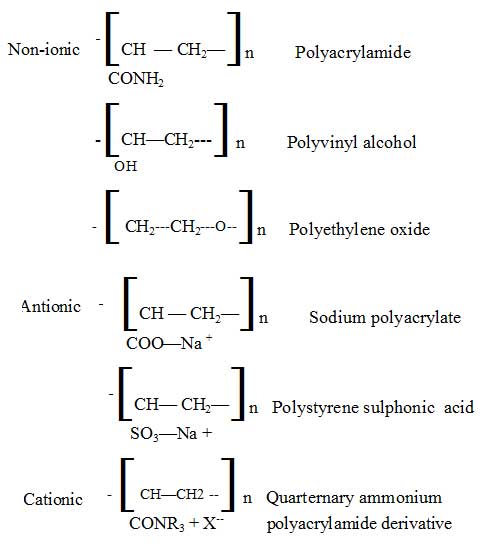
They are water soluble anionic, cationic, non ionic polymers . Non ionic polymers adsorb on the suspended particles The most common natural flocculants are
a) Starch derivatives: Mostly pregelatinized hence water soluble . They are corn or potato, starch are natural starches, anionic oxides starches or amine treated cationic starches . They used of this classes of product has decreased in water treatment but remain important in the paper industries .
b) Polysaccharides: Usually guar ,gums & mostly used in acidic medium .
c) Alginate: Anionic & used in potable water treatment
Synthetic flocculants:
Polyacrylamides: The most common polymers are those based on Polyacrylamide. Which is a a nonionic polymer. Their effect is due to bridging between particles polymer chains. Polymer can be given anionic character by co polymerizing acrylmide with acryl amide acid,. Cationic polymer are prepared by co polymerizing acryl amide with a cationic monomer. All available acryl amide based polymers have a specific amount of ionic monomer giving a certain degree of ionic characters.
Action of flocculants:
a) Dispersion of polymer in solution phase.
b) Transport of polymer to solid phase.
c) Adsorption of polymer on solid surface.
d) Collision of particles being adsorbed polymer to permit formation.
Advantages of flocculants in clarification:
a) Rate of settling is fast.
b) Batter compactness in mud.
c) Improved clarity of juice.
d) Reduction in color formation and mud volume.
e) Due to thickening of mud lesser sugar loss in filter cakes.
f) Efficiency of vacuum filter improve.
g) Clarifier capacity increased by 10-20 %.
h) 0.3 to 0.5 rise in purity achieved from mixed juice to clear juice.
i) Reduction in filter cake pol by 0.3 to 0.5 units.
Flocculents in sugar industry:
a) A number of synthetic flocculating agents are using in the sugar industry clarification process. These flocculants are synthetic high molecular weight polyacrylamides which are partially hydrolysed. Their efficiency as settling aids depends on the molecular weight which ranges between 7 to 10 million and the degree of hydrolysis.
b) These compounds serve as bridges among particles of precipitate and thus bring about formation of bigger aggregates of flocs.
c) The most common flocculants used for juice clarification as well as filter feed conditioning are hyolyzed polyacrylamide compounds, Which are anionic types. Cationic type of flocculents have much more limited use, mainly as decolorants in syrup flotation processes.
d) They are added as 0.05 % concentrated solution in water at the rate of 1.5 to 5 ppm on juice,
e) The dosing to be connectec to the treated juice in the pipe connecting flash tank to clarifier.
f) In the trayless clarifier has reduced the time of juice retention to 45 to 60 minutes. For improving settling rate and increasing the clarifier through put the addition of synthetic flocculant is essential.
g) Thus the introduction of synthetic polyacrylamide as settling aids has been a significant advance in the process of clarification.
Flocculant Properties:
| Property | Effects |
| Molecular weight increase | Poor solubility, more viscous solutions, chain more shear sensitive, Higher unit cost, Higher optimum dose, bridging favored, large flocs and faster settling but higher sediment volume |
| Temperature Change | Complex effects |
| Dose increase | Better flocculation up to optimum |
| Shear increase | Breakdown of long chain, irreversible |
| Particle surface area increase | Increase flocculants consumption, ultra fines, susceptible to over dosing and restabilisation. |
| Suspension pH | Non ionic little affected, ionization and extension of anionic at alkaline pH- converse for catatonics, also alters particle charge, combined effects on flocculation are complex. |
| Suspension ionic strength | Similar to suspension pH- can promote or inhibit flocculation, Excess salt lowers solubility, coils polymer |
| Polymer charge density increase | Extends polymer solution under suitable conditions, decrease adsorption on to particle of same sign. |
Clarification in sugar process:
a) The clarification step in sugar manufacture is designed to remove insoluble suspended impurities from the mixed juice .
b) The formation of cane juice floc is based on Ca3(PO)4 and protein. Its effective density is varied by surface charge effects (Zeta potential).
c) Flocculation has been described by Crees et al. as a two-stage reaction, the first step being the scavenging of individual particles into micro flocs, and the second being the agglomeration of these into macro-flocs that settle relatively rapidly.
d) The nature of colloid particles must be collected into agglomerates. The intended effect of juice clarification by sedimentation is to achieve 1. higher clarity of juice 2. compact volume of mud.
e) The higher clarity of juice means fewer suspended solids. Flocculants improve juice clarity by decreasing suspended solids. The compactness of mud can reduce the retention time of juice inside the clarifier thus reducing the color formation and also sucrose degradation.
Flocculant preparation and dosing:
a) The flocculant tanks in either stainless steel or suitable MS tank with epoxy painting. This eliminates the potential contact between flocculant molecules and iron, which can quickly result in degraded flocculant.
b) The preparation tank should be located directly above the stock holding tank. The preparation tank having stirrer and its recommended speed of 10-15 rev/min. Otherwise air sparger is one of the best option for preparation of flocculent.
c) Always ensure that in-line valves are fully open when dropping the solution from preparation tank to holding tank. Because molecules will be sheared if the solution is passed through partially open valves.
d) It having two tanks are sized to provide 4 to 8 hours supply of 0.05% to 0.2% concentration. The flocculant demand equivalent to 1.5 to 4 ppm on juice. The concentarion and dosing ppm may be veariy according to type of clarifier and dosing process. The final dosing solution concentarion to be maintain 0.05%.
e) A minimum of four hours of preparation should be allowed before the flocculant solution is dropped to the holding tank. A mixing time of two hours should be considered as the absolute minimum mixing time and should only be adopted as an emergency procedure.
f) The water supply must be of good quality with a pH greater than 8, of low hardness and be less than 50ºC. It is recommended that cooled condensate with 8 pH.
g) It is essential that all the flocculant powder is wetted before reaching the water in the mixing tank to prevent the formation of large lumps or ‘oysters’ of flocculant, which are difficult to dissolve fully, and can block pipes and screens.
h) Suitable disperser units consist of a funnel hopper and a variable aperture arrangement designed to ensure wetted individual particles of flocculant powder.
i) Flocculant solution will become ineffective after 18 hours, so fresh solution must be prepared after a long process stoppage.
j) The most suitable pump for flocculant is a progressing cavity pump operating at slow speeds with a variable frequency drive.
k) In some designers flocculant preared by 0.2% concentration and the dilute to 0.03 to 0.05% solution by inline mixer with condensate water or clear juice while solution passing from flocculent pump to flash tank. It will helpful to increase the useful life of the flocculant and reduce the water dilution.
Flocculant preparation and holding tank volume and dosing pump calculation.
In this we take one example and find the above parameters.
| Flocculant Dosing for clarifier | |||||
| S.No | Description | Sign | Values | UOM | Remarks |
| 1 | Crushing rate | TCH | 210 | TCH | |
| 2 | Flocculant Dosing | R | 2 | PPM | |
| 3 | Concentration of flocculant | C | 0.05 | % | 0.05 to 0.2 % |
| 4 | Retention time | T | 4 | hrs. | 4 to 8 hrs. |
| Calculation | |||||
| 1 | Flocculant Quantity | Q = TCH x R / 1000 | 0.42 | Kg/hr | |
| 2 | Flocculent flow rate | Qr = Q x 100/ C | 840 | Lt/ hr | |
| 3 | Pump capacity required | Qr x 1.1 | 924 | Lt/ hr | 10% extra |
| 4 | Preparation tank capacity | (Qr x T/1000) x 1.1 | 3.696 | M3 | 10% extra |
| 5 | Holding or stock tank capacity | (Qr x T/1000) x 1.2 | 4.032 | M3 | 20% extra |
Flocculant Dosing Online Calculator
Related Articles
Sugar Process Industry Terminology in Clarification section like Imbibition, Bagacillo,Bagasse,Cush Cush,Fiber,Lime,Flocculent,Affination,Raw Juice etc.
Phosphoric Acid(H3PO4) in sugar process industry and online calculator to find required dosing quantity in kgs and also find present going condition in PPM.
Juice Clarifier Flash Tank design parameters like dia of the flash tank, juice inlet and out line sizing, flash vent pipe sizing ..etc.with online calculation sheet.
Sugar Tech | Sugar Technology related articles with online calculators
Hi friends Thanks for reading. I Hope you liked it. Give feed back, comments and please share it.

22 thoughts on “Flocculants Used in Sugar Processing | Flocculant Dosing Calculation”
DAYANAND HIREMATH
(October 4, 2017 - 4:55 pm)Nice information
siva alluri
(October 4, 2017 - 5:35 pm)Thank you sir
Hazen elmasry
(October 25, 2017 - 9:20 pm)Give me more details about floculation and sedimentation of cane sugar juice with cationic and anionic co_polymer or home polymer
siva alluri
(October 27, 2017 - 2:07 pm)Ok sir
we will provide in separate article for that
Clarifier setting process.
If you having knowledge related to this topic please submit in word doc. we will publish according to your good name.
Contact mail: sugarprocesstech@gmail.com
Thank you
krishna toragal
(November 1, 2017 - 1:00 am)nice topic
siva alluri
(November 1, 2017 - 1:01 pm)Thank you sir
The “www.sugarprocesstech.com” invites to all sugar technologists to share your knowledge, achievements in your working organization and new developments and technologies in sugar industry and its concerned units. It is very much helpful to show your identity to the world at the same time it will helpful to another technologist to enhance their insight and enhance great execution in there working. This website also provides the basic knowledge in sugar industry technologies and equipment design calculation with online calculators.
sugarprocesstech@gmail.com
krishna toragal
(November 1, 2017 - 1:01 am)nice
Umakant Paul
(January 30, 2018 - 12:36 am)Sir I want Refinery Telo clarifier calculation and FFE calculation
siva alluri
(January 30, 2018 - 1:36 pm)Mr.Umakant
Definitely we will provide soon melt clarification system calculation
Ramadhan Salehe Sal-min
(May 11, 2023 - 12:09 pm)I would like to get more information regarding the formula used in calculating Quantity of flocculant.
Here is the formula used:
Q=(0.42×TCH×R)/1000 where R is the dosing ppm
Can someone tell me where 0.42 is coming from. Or someone to drive a formula
Kennias Musasa
(March 16, 2018 - 6:57 am)well explained.
siva alluri
(March 23, 2018 - 4:58 pm)Thank you Mr.musasa
narendra jain
(April 13, 2018 - 10:15 am)well explained to learners and useful for professionals also as it is online available.
siva alluri
(April 16, 2018 - 1:21 pm)Thank you Mr.jain
Surendra singh
(April 28, 2018 - 8:45 am)Sir,please tell me about short retention time clarifier design and calculation all about it.
siva alluri
(May 3, 2018 - 2:42 pm)Ok Mr.Surendra
We will publish soon
Goutam Buddha
(July 23, 2018 - 10:27 am)Thank you sir for the A -Z information about sugar process
siva alluri
(July 25, 2018 - 1:57 pm)Thank you my dear Goutam Buddha
Vijay Narade
(July 30, 2018 - 9:33 am)Nice article.
siva alluri
(August 13, 2018 - 2:37 pm)Thank you
Nitin C Naik
(January 5, 2023 - 2:16 pm)Kindly let me know the usages of Magnafloc LT 27 in sugar refining process. Like what is the action of the product on sugar cane juice wrt clarity, compaction, settling rates and so on.
This is my first job profile in chemical products- Sales out of total 25 years of experience.
Of course all the last years I have spent in power transmission products, ie purely mechanical engineering. So request to kindly help me.
Thanks and regards Nitin C Naik Hospet. Karnataka
Ramadhan Salehe Sal-min
(May 11, 2023 - 12:08 pm)I would like to get more information regarding the formula used in calculating Quantity of flocculant.
Here is the formula used:
Q=(0.42×TCH×R)/1000 where R is the dosing ppm
Can someone tell me where 0.42 is coming from. Or someone to drive a formula